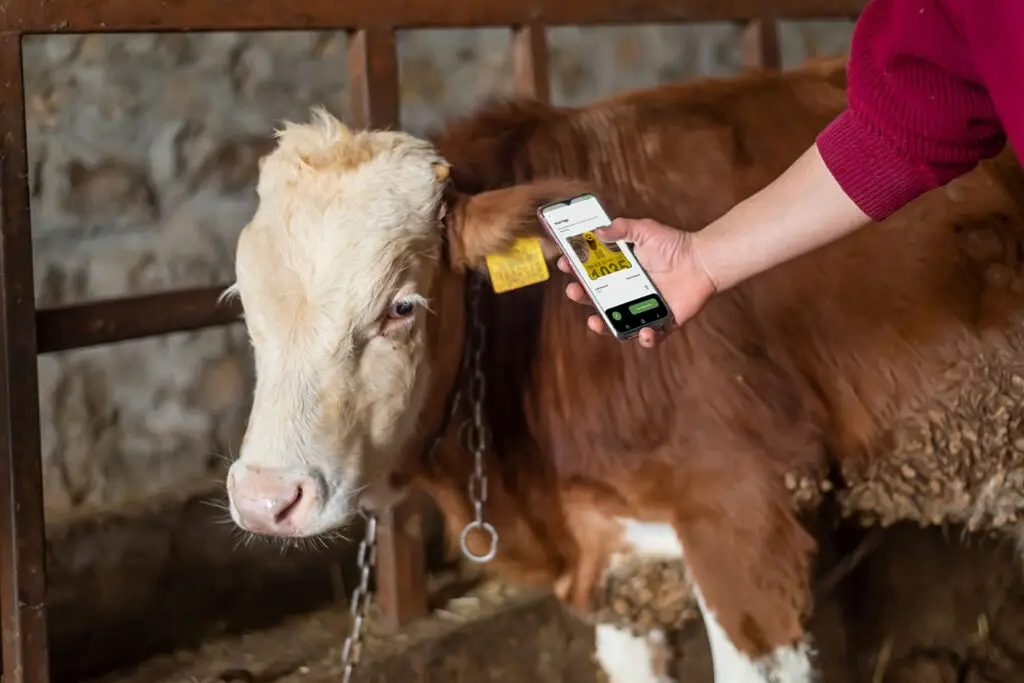

RFID in Animal Identification: Enhancing Livestock Management & Pet Tracking
Traditional methods of animal identification (ear tags, tattoos, or manual records) are prone to errors, loss, or tampering. Farmers, veterinarians, and pet owners struggle with accurate tracking, health monitoring, and regulatory compliance.
RFID-based animal identification enables automated tracking, health record management, theft prevention, and regulatory compliance, improving overall efficiency in livestock farming, pet ownership, and wildlife conservation.
How RFID is Used in Animal Identification:
1. Livestock Tracking & Herd Management
- Animals (cattle, sheep, pigs, etc.) are fitted with RFID ear tags or injectable RFID microchips.
- RFID readers at farm gates, feeding stations, and veterinary checkpoints automatically scan animals.
- Farmers can track birth records, vaccinations, breeding cycles, and weight gain/loss in real time.
- Reduces manual labour and improves herd efficiency.
2. Pet Identification & Lost Pet Recovery
- RFID microchips (ISO 11784/11785 compliant) are implanted under a pet’s skin.
- Veterinary clinics and shelters scan RFID chips to retrieve owner contact details.
- Helps reunite lost or stolen pets with their owners.
3. Disease Control & Biosecurity Compliance
- RFID helps in monitoring disease outbreaks by tracing infected animals.
- Governments enforce RFID-based animal ID programs to meet regulations (e.g., USDA’s Animal Disease Traceability program, EU Livestock Tracking).
- Allows rapid quarantine and movement control of infected livestock.
4. Wildlife & Endangered Species Monitoring
- RFID tags help in tracking migration patterns, population studies, and anti-poaching efforts.
- Used in conservation programs for species like rhinos, elephants, birds and also Fish.
- Helps researchers collect long-term ecological data.
5. Automated Feeding & Milking in Dairy Farms
- RFID-enabled feeding stations allow automated feed dispensing based on each animal’s nutritional needs.
- Dairy farms use RFID to identify cows during milking, ensuring proper recordkeeping of milk production.

There are many use cases that are referred to as Industrial typically all Industrial use cases will use
Compliance and Audits
RFID logs provide audit trails to prove that inspections and services were performed.
Helps meet regulatory and safety compliance requirements.
Equipment Tagging
Each piece of equipment is fitted with an RFID tag (passive or active).
The tag contains a unique identifier and can store data such as maintenance history, serial numbers, or inspection dates etc.
Scanning and Data Collection
Inspectors use an RFID reader (handheld or fixed) to quickly scan the tag.
The reader retrieves data from the tag (Or the supporting Software system, often cloud based) and updates the system with inspection results, service status, and technician notes
Automated Record Keeping
Inspection and service details are recorded in a centralized database.
Eliminates the need for manual logging, reducing human errors.
Scheduled Maintenance Alerts
The system can trigger automatic reminders for periodic inspections or servicing.
Ensures equipment is maintained on time, preventing breakdowns.
Real-time Equipment Tracking
RFID tags help track equipment location in large facilities or remote sites.
Useful for managing tools, safety gear, or heavy machinery.
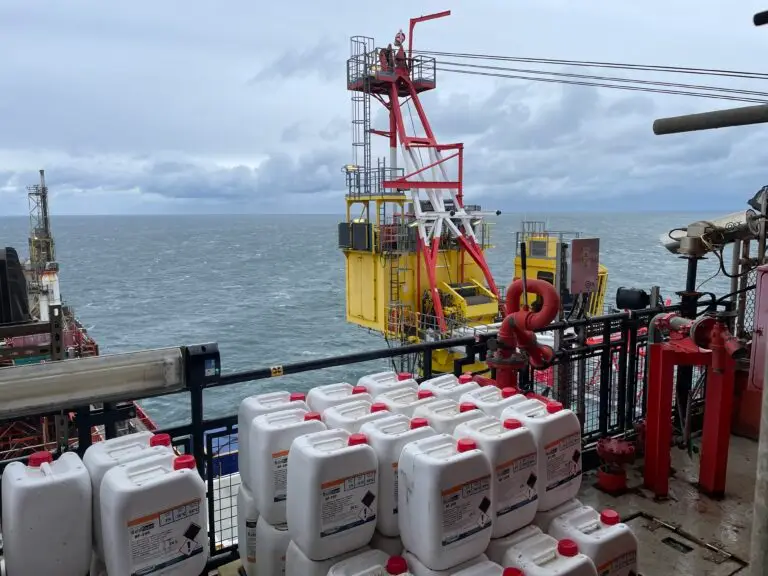

RFID Use Case in Offshore Oil & Gas: Equipment Inspection & Maintenance
Offshore oil and gas platforms operate in harsh environments where equipment failures can lead to costly downtime, safety risks, and environmental hazards. Traditional paper-based inspection records are inefficient, error-prone, and difficult to track and communicate when compared to the digital efficiencies of RFID.
Implement an RFID-based inspection and maintenance system for offshore equipment like valves, pipes, pressure vessels, lifting gear, and fire safety equipment, supporting efficiency and compliance.
How RFID is Used in Offshore Oil & Gas:
1. Tagging Equipment & Assets
- RFID tags are attached to critical equipment (e.g., pipelines, pumps, safety gear, and lifting tools).
- The tags contain unique IDs linked to a database with maintenance history, inspection schedules, and compliance certifications.
2. Automated Inspection & Maintenance Tracking
- Inspectors use a rugged handheld RFID reader to scan tagged equipment.
- The reader instantly retrieves inspection history, pending service alerts, and compliance data.
- After servicing, technicians update the tag via the RFID system, ensuring real-time recordkeeping.
3. Predictive Maintenance & Alerts
- The RFID system tracks service intervals and sends automated alerts when maintenance is due.
- Helps prevent equipment failures and unplanned downtime.
4. Real-time Asset Tracking & Inventory Management
- RFID tags can help locate tools and spare parts on large platforms, and provide detailed logs of who has what.
- Reduces time wasted searching for critical assets during repairs.
5. Compliance & Safety Audits
- RFID logs provide digital proof of inspections for regulatory compliance (e.g., API, OSHA, ISO 14224).
- Auditors can access complete maintenance records instantly, reducing paperwork.

Returnable Transport Items (RTIs), such as pallets, crates, containers, kegs, and roll cages, are frequently lost, misplaced, or underutilised, leading to high replacement costs, inefficiencies, and tracking difficulties. Manual tracking methods are error-prone and time-consuming, affecting supply chain visibility.
RFID-based RTI tracking enables real-time visibility, automated inventory management, and efficient return processes, reducing losses and optimising supply-chain logistics.
How RFID is Used in RTI Management:
1. RTI Identification & Tracking
- Each RTI is fitted with an RFID tag (usually UHF for long-range tracking).
- RFID readers installed at warehouses, docks, and retail locations automatically track RTI movements.
- Provides real-time location updates, ensuring RTIs are used efficiently and returned on time.
2. Automated Check-in/Check-out & Inventory Management
- RFID gates at loading docks and distribution centers automatically log RTIs entering or leaving.
- Eliminates manual scanning, reducing human errors and speeding up operations.
- Helps businesses track which customers or suppliers have their RTIs.
3. Loss Prevention & Asset Utilization Optimization
- RFID systems alert companies when RTIs fail to return within a set timeframe.
- Data analytics help optimize RTI allocation, ensuring availability when needed.
- Helps reduce excess RTI inventory and minimize unnecessary purchases.
4. Billing & Deposit Refund Automation
- RFID-enabled RTIs allow for automated deposit/refund processing based on returns.
- Ensures customers return containers, pallets, or crates within agreed timelines.
- Common in beverage and food industries where keg and crate deposits are standard.
5. Temperature & Condition Monitoring (for Perishables & Sensitive Goods)
- Smart RFID tags can monitor temperature, humidity, or shock impact during transport.
- Ensures food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals remain within safe conditions.
- Provides a digital audit trail for compliance and quality assurance.
Traditional packaging lacks real-time tracking, product authentication, and interactive customer engagement. Counterfeiting, supply chain inefficiencies, and waste management are common challenges.
RFID-integrated smart packaging improves traceability, security, and consumer interaction by embedding RFID tags into product packaging.
How RFID is Used in Smart Packaging:
1. Real-Time Supply Chain Tracking
- RFID tags embedded in packaging enable real-time tracking from manufacturing to retail.
- Retailers and distributors use RFID readers to scan multiple items at once, improving inventory management.
- Helps in anti-theft measures and automated stock replenishment.
2. Product Authentication & Anti-Counterfeiting
- RFID provides unique digital IDs that verify product authenticity.
- Luxury goods, pharmaceuticals, and high-value electronics use RFID to combat counterfeiting.
- Customers or retailers can scan RFID tags via NFC-enabled devices to confirm genuineness.
3. Consumer Engagement & Smart Labels
- RFID NFC (Near Field Communication) tags allow consumers to access digital content by tapping their smartphones on the packaging.
- Brands can offer product information, promotions, loyalty programs, or interactive experiences.
- Example: A wine bottle with an RFID tag can provide details on origin, tasting notes, and food pairings via a mobile app.
4. Cold Chain Monitoring (Perishable Goods & Pharmaceuticals)
- RFID tags with temperature and humidity sensors (Usually these would be Active Tags) track conditions during transport and storage.
- Ensures that food, vaccines, and biologics remain within safe temperature ranges.
- Alerts suppliers if temperature thresholds are breached.
5. Automated Checkout & Smart Retail
- RFID enables self-checkout by allowing customers to place RFID-tagged products in a scanner without manual barcode scanning.
- Reduces checkout time and improves the shopping experience.
6. Sustainable Packaging & Waste Management
- RFID-enabled smart bins help sort recyclable packaging materials.
- Governments and businesses use RFID to track waste and encourage sustainable practices
The Internet of Things (IoT) relies on devices communicating with each other, but traditional tracking and identification methods (barcodes, QR codes, manual entry) are inefficient, prone to errors, and lack real-time automation. Many industries struggle with asset tracking, supply chain transparency, and automation.
RFID enables seamless IoT integration by providing real-time tracking, automation, and data collection across various industries, enhancing efficiency, security, and analytics in smart environments.
How RFID is Used in IoT:
1. Smart Asset Tracking & Inventory Management
- RFID tags embedded in or applied onto assets (e.g., tools, equipment, products) allow for real-time tracking.
- IoT-enabled RFID readers and sensors collect and transmit location/status, Date & Time data to cloud-based platforms.
- Used in warehouses, hospitals, retail, and logistics for automated stock control and loss prevention.
2. Supply Chain & Logistics Optimization
- RFID tags track goods from manufacturing to final delivery, ensuring real-time visibility.
- IoT-connected RFID readers update shipment conditions, delays, and inventory levels.
- Temperature & humidity sensors in RFID tags monitor perishable goods like food and pharmaceuticals.
3. Smart Manufacturing & Industry 4.0
- RFID-tagged components in factories allow automated production line tracking.
- IoT-integrated RFID systems trigger machine adjustments, maintenance alerts, and process automation.
- Predictive maintenance reduces downtime by monitoring machine parts for wear and tear.
4. Smart Cities & Infrastructure Management
- RFID in IoT is used for traffic monitoring, parking systems, and smart waste bins.
- Cities use RFID sensors to track public transportation, road tolling, and fleet management.
- Helps optimize urban planning, energy use, and sustainability efforts.
5. Healthcare & Patient Monitoring
- Hospitals use RFID-based IoT systems for real-time tracking of medical equipment, patient records, and staff movements.
- RFID-enabled wristbands provide automated patient identification, reducing errors in treatment.
- Monitors medication usage, inventory levels, and compliance in smart pharmacies.
6. Smart Homes & Retail Experiences
- RFID-enabled IoT systems in smart homes automate access control, appliance tracking, and security.
- In retail, RFID-powered smart shelves track inventory and notify staff about restocking.
- Checkout-free stores (like Amazon Go) use RFID to detect what customers pick up and charge them automatically.

Many industries lack full lifecycle transparency for products, making it difficult to track origin, ownership, repairs, and recycling. This results in waste, inefficiencies, and difficulty meeting sustainability regulations like the EU’s upcoming Digital Product Passport (DPP) initiative.
RFID-enabled Digital Product Passports (DPPs) store and update detailed product lifecycle data in a digital record linked to each item, improving traceability, compliance, and sustainability.
How RFID is Used in Digital Product Passport:
1. Unique Product Identity & Lifecycle Tracking
- RFID tags (UHF, NFC, or HF) are embedded in products, linking them to a cloud-based digital passport.
- Each RFID tag contains a unique digital ID (EPC – Electronic Product Code) that stores and updates manufacturing data, materials used, repair history, ownership records, and recycling instructions.
- Enables real-time tracking from production to disposal.
2. Authentication & Anti-Counterfeiting
- Consumers, retailers, and regulators can scan RFID/NFC tags to verify a product’s authenticity and provenance.
- Particularly valuable for luxury goods, pharmaceuticals, and high-end electronics to prevent counterfeiting.
3. Circular Economy & Sustainability Compliance
- RFID enables materials traceability, helping brands comply with EU sustainability regulations (e.g., Green Deal, Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation – ESPR).
- Assists in recycling and repurposing by providing details on material composition and disassembly instructions.
- Example: A fashion brand using RFID in DPPs allows second-hand marketplaces to verify materials, care instructions, and previous ownership.
4. Repair, Resale & Warranty Management
- RFID-powered DPPs store repair and maintenance history, making it easier to service and resell products.
- Manufacturers can use RFID to enable automated warranty verification.
- Example: A smartphone DPP can show past repairs, battery health, and official warranty status when resold.
5. Consumer Engagement & Smart Labeling
- NFC-enabled RFID tags allow consumers to access DPP data via smartphones.
- Users can see usage tips, eco-footprint, and recycling incentives.
- Brands can incentivise customers with return and recycling rewards using RFID scans.
